What is Alcohol Poisoning?
Alcohol poisoning can strike after rapid heavy drinking and may be life threatening learn how to spot danger signs and when to seek emergency help immediately
Talk to our admissions team
Alcohol poisoning can happen when someone drinks too much too quickly, like during a binge. Your body can only handle so much alcohol at a time, and if you drink more than it can process, the alcohol builds up in your system. This can mess with critical things like your breathing, heart rate, body temperature, and even your ability to cough or vomit to protect yourself.
In severe cases, it can lead to a coma or even be fatal. It’s a very serious condition and can be life-threatening.
What to do if you drank too much alcohol?
Make sure to drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated—water, sports drinks like Gatorade® or Pedialyte®, or even some broth can help. Try to drink enough so that your urine is clear, which shows you’re well-hydrated. Get plenty of rest to help with tiredness, and if your stomach feels upset, an antacid can help calm it down. Just remember, the more you drink, especially quickly, the greater the chance of alcohol poisoning.
Why does someone vomit after drinking alcohol?
Alcohol can upset your stomach and make it produce more acid, which can cause discomfort, nausea, or even make you throw up. If someone ends up vomiting after drinking, it’s just the body’s way of getting rid of the harmful stuff in the alcohol. It’s a natural reaction to help clear out the toxins.
What to eat after alcohol poisoning?
“This is what’s called the ‘BRAT’ diet,” says Zumpano. “Bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast.” These easy-to-digest foods are gentle on your stomach and are often suggested when you’re not feeling well—especially if you have an upset stomach, diarrhoea, nausea, or are struggling to eat or keep food down.
Is coke good for a hangover?

Some people swear by a can of Coke, a cup of tea, or black coffee to feel better, but it only helps for a short time. A hangover is your body being dehydrated, and caffeine can actually make it worse by drying you out more. After drinking too much, you’re often left feeling tired or not getting enough rest. In that case, coffee or something with caffeine can help you feel a little more awake and ease that headache.
What not to eat after drinking too much alcohol?
Try to stay away from greasy foods, sugar, and caffeine, as they can make your symptoms worse. Instead, focus on drinking water, electrolyte drinks, and eating bland foods like bananas and crackers.
Understanding Alcohol Poisoning
Alcohol poisoning is a dangerous condition that can occur when someone drinks too much alcohol too quickly. It can lead to serious health problems and even death if not treated promptly.
Defining Alcohol Poisoning
Alcohol poisoning happens when a person’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) becomes dangerously high. This occurs when the liver cannot process alcohol quickly enough, leading to a build-up of toxins in the body. The type of alcohol that causes poisoning is ethanol, found in beer, wine, and spirits.
Alcohol poisoning is different from being drunk. It’s a severe medical emergency that can cause lasting damage to the brain and other organs. The body treats alcohol as a poison, so drinking too much can overwhelm the system.
Identifying Symptoms of Alcohol Poisoning
Spotting the signs of alcohol poisoning is crucial. Common symptoms include:
- Confusion and disorientation
- Vomiting
- Seizures
- Slow or irregular breathing
- Blue-tinged or pale skin
- Low body temperature
- Unconsciousness or passing out
A person with alcohol poisoning may not show all these signs. If someone is unresponsive and you can’t wake them, it’s vital to get medical help right away. Alcohol poisoning can lead to choking if a person vomits while unconscious, as their gag reflex may not work properly.
Evaluating Causes and Risk Factors
The main cause of alcohol poisoning is binge drinking, which means drinking a lot of alcohol in a short time. Factors that increase the risk of alcohol poisoning include:
- Drinking games or challenges
- Lack of food in the stomach
- Mixing alcohol with other drugs
- Low body weight or size
- Tolerance levels
- Speed of alcohol consumption
Young adults and teenagers are at higher risk because they may not understand their limits. People with alcohol use disorders are also more likely to experience alcohol poisoning due to frequent heavy drinking.
It’s important to note that alcohol content varies between drinks. Strong spirits can lead to poisoning more quickly than beer or wine. Knowing your limits and drinking responsibly is key to avoiding this dangerous condition.
Medical Response to Alcohol Poisoning
Alcohol poisoning requires immediate medical attention. Quick and proper treatment can mean the difference between life and death for someone with severe alcohol intoxication.
Emergency Treatment Procedures
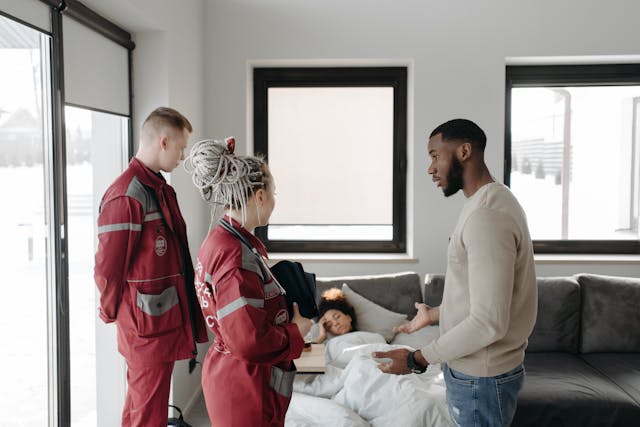
When someone shows signs of alcohol poisoning, call 999 immediately. While waiting for help, keep the person awake if possible and in a sitting position. If unconscious, place them in the recovery position to prevent choking on vomit.

Emergency responders will assess vital signs and level of consciousness. They may provide oxygen to help with breathing difficulties. At the hospital, doctors may perform:
• Intravenous (IV) fluids to prevent dehydration • Blood sugar monitoring and glucose if needed • Vitamins and minerals to prevent complications • Gastric lavage (stomach pumping) in some cases
Severe cases may require intubation to protect airways or dialysis for alcohol removal.
Alcohol Poisoning Diagnosis
Diagnosing alcohol poisoning involves several steps:
- Physical exam to check vital signs
- Blood tests to measure alcohol levels
- Urine tests for drugs or other substances
- Glucose checks for low blood sugar
Doctors will also look for signs like:
• Slow or irregular breathing • Low body temperature (hypothermia) • Confusion or unresponsiveness • Seizures
They’ll rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as diabetic coma or head injury.
Treatment and Recovery Options
Treatment for alcohol poisoning aims to manage symptoms and prevent complications through a medical detox. This may include:
• Continued IV fluids and electrolytes • Thiamine (vitamin B1) to prevent brain damage • Medications to stop vomiting • Close monitoring of vital signs
Recovery time varies based on severity. Some people improve within 24 hours, while others may need several days of hospital care.
After discharge, follow-up care is crucial. This might involve:
• Substance abuse counselling • Alcohol rehab treatment • Liver function tests • Assessment for alcohol dependence
Long-term recovery often requires addressing underlying alcohol use issues to prevent future episodes.
Preventing Alcohol Poisoning
Avoiding alcohol poisoning involves understanding how many drinks are too many, strategies to prevent excessive alcohol use, and recognising warning signs. These measures can help reduce the risk of severe health consequences and potential fatalities associated with excessive drinking.
Educating on Safe Alcohol Consumption
Safe alcohol consumption involves knowing personal limits and understanding how alcohol affects the body. It’s crucial to be aware of standard drink sizes and recommended daily intake.

For men, no more than 3-4 units per day is advised. Women should limit intake to 2-3 units daily. One unit equals:
- 25ml of spirits (40% alcohol)
- 76ml of wine (13% alcohol)
- 250ml of beer (4% alcohol)
Spacing drinks over time and alternating with water helps maintain control. Eating before and during drinking slows alcohol absorption.
It’s important to understand that alcohol tolerance varies. Factors like body weight, metabolism, and overall health influence how quickly one becomes intoxicated.
Strategies to Avoid Overconsumption
To avoid alcohol poisoning, implement these strategies:
- Set a drink limit before going out
- Drink slowly, sipping rather than gulping
- Choose lower-alcohol beverages
- Avoid drinking games or competitions
- Don’t mix alcohol with energy drinks
Stay hydrated by drinking water between alcoholic drinks. This helps slow consumption and reduces dehydration.
Designate a sober friend to monitor drinking levels. They can intervene if someone shows signs of overconsumption.
Avoid pressuring others to drink. Respect those who choose not to consume alcohol or wish to stop drinking.
Recognising Alcohol Poisoning Signs and Interventions
Recognising alcohol poisoning symptoms is crucial for timely intervention. Key signs include:
- Confusion or stupor
- Vomiting
- Seizures
- Slow or irregular breathing (less than 8 breaths per minute)
- Pale or bluish skin
- Low body temperature
- Unconsciousness or inability to wake up
If these signs are observed, take immediate action:
- Call emergency services
- Keep the person awake if possible
- Turn them on their side to prevent choking if vomiting occurs
- Do not leave them alone
Never assume someone will ‘sleep it off’. Alcohol poisoning can lead to brain damage or death if left untreated. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent serious complications.






